Remote Weather Stations: Features, Benefits and Applications
Remote Weather Stations: Benefits and Applications
Have you ever considered how mines, farms, construction sites, maintain awareness of the weather even in remote locations? Enter remote weather stations, the sophisticated tools that serve as invaluable meteorological companions.
Remote weather stations are miniature meteorologists, strategically positioned to provide real-time local information. Managers of mines, farms and construction sites use this information to stay ahead of unpredictable weather patterns.
From forecasting rain for a farm to ensuring safety in mines, remote weather stations serve as the unheralded guardians of remote areas. Lets explore the realm of remote weather stations and uncover the intricacies of weather forecasting in remote areas.
Understanding Remote Weather Stations
Remote weather stations include several specialized sensors to measure wind speed and direction, rainfall, sun intensity, temperature, humidity and atmospheric pressure. These sensors are connected to a sophisticated data logger that collects and transmits real-time weather data to a customer. This information can be transmitted my WiFi, public of private 4G networks, or Ethernet.
These stations offer a reliable means of monitoring critical environmental conditions. The data collected is instrumental in making informed decisions, optimizing resource usage, and enhancing overall productivity.
Operational Benefits
The adoption of remote weather stations brings about operational benefits that extend beyond data collection. Enhanced efficiency, resource optimization, and improved safety are among the key advantages.
- Rainfall data enables farmers to implement targeted irrigation, reducing water usage and minimizing environmental impact
- Real-time wind speed information can inform decisions on using cranes or air strips
- Barometric pressure data can be used to forecast incoming storms
- Temperature and humidity data can be used to make decisions on pouring concrete and employee well-being
- In mining, where machinery operates in harsh conditions, temperature data can inform maintenance schedules for equipment
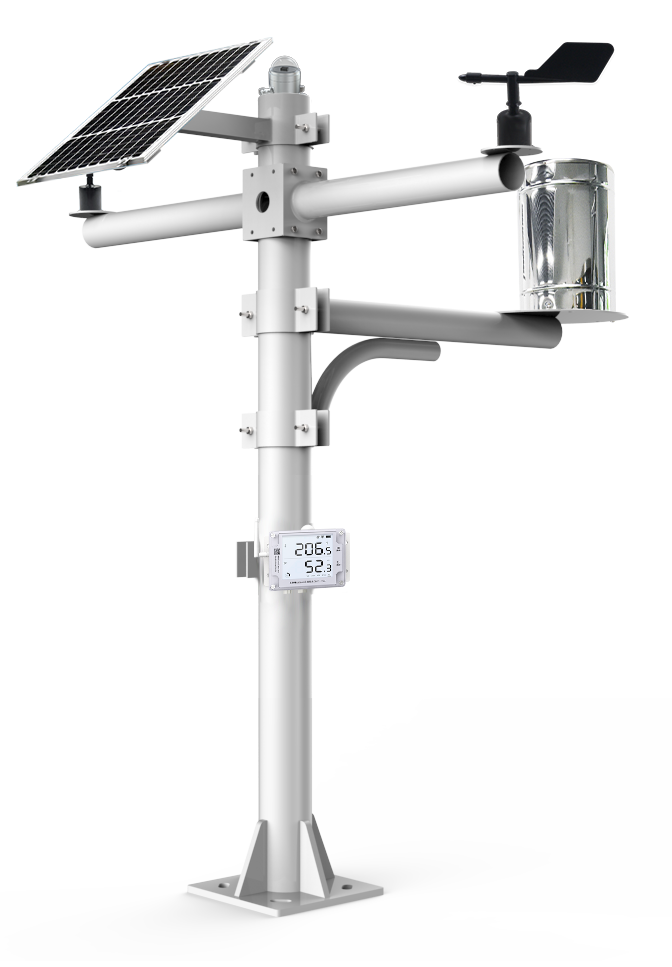

Components of a UbiBot Remote Weather Station
GS1 Data Logger
The core of a remote weather station is the GS1 wireless temperature data logger. This device ensures accurate and continuous monitoring of weather variations both mining and farming environments. The GS1 data logger connects to your network with ethernet, WiFi, or SIM/ 4G and has on-board temperature and humidity sensors.
In addition to the on-board sensors, you can connect up to five (5) external sensors to complete your remote weather station. Some models even have a IP65 waterproof rating so they can mounted outside.
Powering Your Remote Weather Station
You have several options for powering your remote weather station including using the internal lithium ion Battery, 12V power supply or a solar panel and 12V external battery.
The choice will depend on your specific requirements. The internal battery will last from 2 or 3 weeks to 4 months depending on the network connection (WiFi or SIM), environmental conditions, number of connected probes and the frequency with which the GS1 transmits to the cloud.
A 12V power supply is reliable but, like the built-in battery not practical for many remote locations. A solar panel and 12V battery is ideal as installation is simple and hard-wired power is not required.
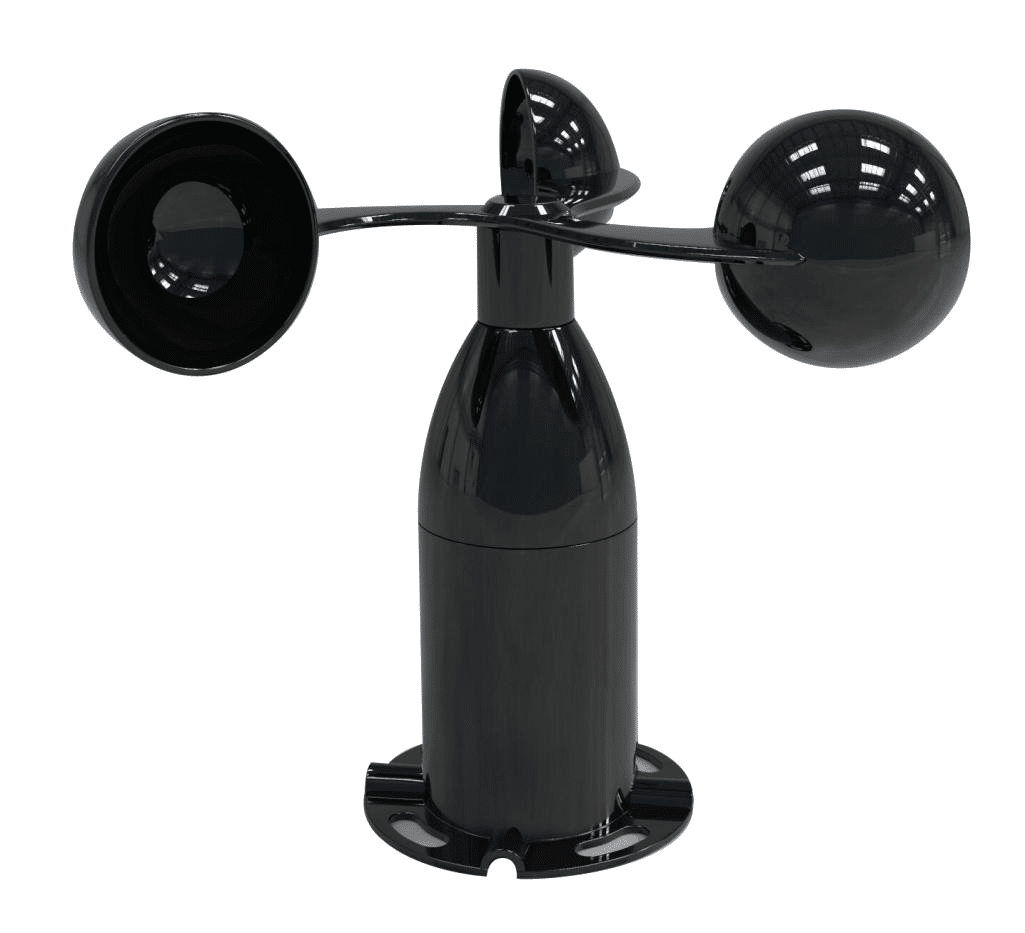
Wind Speed Sensor and Wind Direction Sensor
Wind plays a pivotal role in both mining and agriculture, influencing factors such as dust dispersion in mines and pesticide and fertilizer spraying at farms.
Regardless of your application, wind sensors are integral to any remote weather station. UbiBot’s wind speed sensor and wind direction sensor are ideal partners for to provide real-time data on wind patterns.
These sensors operate on different mechanisms as they measure different aspects of wind conditions. Both sensors are needed to ensure that you have a complete view of wind conditions.


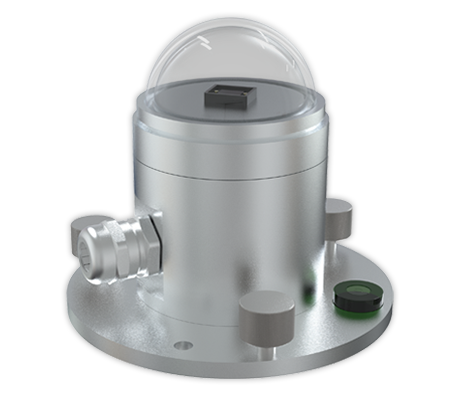
Barometric Pressure Sensor
Barometric pressure is a fundamental weather variable. A barometric pressure sensor, also known as an atmospheric pressure sensor, is crucial if you want to add forecasting capabilities to your weather station.
UbiBot’s atmospheric pressure sensor allows you to monitor changes in air pressure which correlates with changes in weather patterns. Rising barometric pressure signals more stable, calm weather. While falling pressure indicates worsening weather.
Combining barometric pressure data with humidity and temperature data can allow you to forecast frost, snow, storms and changes in wind direction and speed.

Rain gauge and Solar Radiation Sensor
If your business operates in a wet environment or if accurate rainfall data is important to you then a rain gauge may be an important addition to your remote weather station.
UbiBot’s rain gauge, also known as a rainfall sensor, accurately measures rainfall with a resolution of 0.2mm and an accuracy of 0.32mm.
If measuring the intensity of the sun is important, then UbiBot’s solar radiation sensor is perfect. With this sensor you can accurately sun intensity with high accuracy and a fast response time.
Both of these sensors add value to your remote weather station. This is especially true for farms which rely on rain and sunlight data to inform planting and irrigation decisions.


TH30S-B Temperature and Humidity Probe
The GS1 data logger has on-board temperature and humidity sensors. However if the data logger is placed inside a building for easy access, then these on-board sensors will not be able to measure the outside conditions.
This is where an external probe comes into play. UbiBot’s TH30S-B temperature and humidity probe is ideal for this application. You can add this probe alongside the other sensors so that your weather station can provide comprehensive weather information.

Remote Weather Stations: Applications and Benefits
Real-Time Decision-Making and Forecasting
One of the most significant advantages of remote weather stations lies in their ability to provide real-time data. This feature is particularly crucial in environments where conditions can change rapidly. By connecting a barometric pressure sensor to your weather station, you can move from monitoring to forecasting the weather. This enhancement can add significant value to your weather station.
Applications in Mining
Mines often operate in remote areas and challenging environments. The integration of a weather station into these operations can add significant value by providing real-time information on local conditions.
These weather stations provide critical data on temperature, allowing miners to implement measures to prevent overheating of machinery and ensure the safety of personnel. Moreover, wind speed and direction data are crucial in controlling dust, a common challenge in mining activities.
Applications in Agriculture
For farmers, the unpredictability of weather patterns can significantly impact crop yield. Remote weather stations equipped with temperature loggers and solar radiation sensors empower farmers to make informed decisions.
For example, understanding temperature variations helps in selecting the right crops for cultivation, while solar radiation data aids in optimizing irrigation schedules. These stations become invaluable tools for precision agriculture, promoting sustainability and resource efficiency.
Environmental Conservation and Sustainability
The deployment of remote weather stations in mines and farms not only aids in optimizing operations but also contributes significantly to environmental conservation and sustainability. By closely monitoring weather conditions, mining companies can implement measures to minimize their environmental footprint, such as controlling dust emissions and managing water resources efficiently.
In agriculture, the ability to make informed decisions based on real-time weather data promotes sustainable farming practices, reducing the reliance on excessive water usage and chemical inputs. This dual benefit of operational efficiency and environmental stewardship aligns with the growing emphasis on responsible and sustainable business practices.
Data-Driven Predictive Maintenance
In both mining and agriculture, the utilization of data from remote weather stations facilitates a shift toward proactive and predictive maintenance strategies.
For mining equipment exposed to extreme temperatures, the continuous monitoring of temperature variations allows for the identification of potential issues before they escalate, enabling timely maintenance interventions. Similarly, in agriculture, understanding weather patterns helps farmers anticipate and mitigate potential challenges, allowing for preventive measures against crop diseases and pests.
This shift towards data-driven predictive maintenance enhances the overall reliability of equipment and crop yields, contributing to long-term sustainability in both industries.
Conclusion
In the realm of remote weather stations, whether located on mines, farms or any other place, a promising future unfolds. These stations meticulously observe atmospheric conditions, providing essential data for mining and agricultural enterprises to make informed decisions about harvest schedules and workforce safety. The use of advanced technology to monitor and forecast the weather greatly enhances the efficiency and safety of any business.
How Can UbiBot Canada Help with Your Remote Weather Station?
UbiBot Canada is the exclusive Canadian distributor for UbiBot products and we stock the components needed to build your custom remote weather station:
- GS1 environmental data logger
- Robust construction, ideal for wet or dust environments
- Perfect for a remote weather station
- Integral lithium ion battery
- Can also be powered by USB, 12v adapter, ethernet, solar panel
- WiFi, SIM, Ethernet and GPS options
- Compatible with the widest range of external sensors and accessories.
- Atmospheric pressure sensor
- Rain gauge
- Solar radiation sensor
- TH30S-B temperature and humidity probe
- Wind direction sensor
- Wind speed sensor
All UbiBot smart devices are compatible with the UbiBot cloud-based app. In this app, you can:
- View all data from all sensors in real-time
- Analyze historical data
- Set custom alerts based on your chosen thresholds
- Receive these alerts by text, phone, email on in the app
- Connect your UbiBot products to Google Home, Alexa, IFTTT, and Google Sheets
Contact us today if you have any questions or for a quote!
